 |
Taskflow
3.2.0-Master-Branch
|
 |
Taskflow
3.2.0-Master-Branch
|
Unlike tf::Pipeline (see Parallel Pipeline) that instantiates all pipes at the construction time, Taskflow provides a scalable alternative called tf::ScalablePipeline to allow variable assignments of pipes using range iterators. A scalable pipeline is thus more flexible for applications to create a pipeline scheduling framework whose pipeline structure depends on runtime variables.
You need to include the header file, taskflow/algorithm/pipeline.hpp, for creating a scalable pipeline scheduling framework.
Similar to tf::Pipeline, tf::ScalablePipeline is a composable graph object to implement a pipeline scheduling framework in a taskflow. The key difference between tf::Pipeline and tf::ScalablePipeline is that a scalable pipeline can accept variable assignments of pipes rather than instantiating all pipes at construction or programming time. Users define a linear range of pipes, each of the same callable type, and apply that range to construct a scalable pipeline. Between successive runs, users can reset the pipeline to a different range of pipes. The following code creates a scalable pipeline that uses four parallel lines to schedule tokens through three serial pipes in the given vector, then resetting that pipeline to a new range of five serial pipes:
The program defines a uniform pipe type of tf::Pipe<std::function<void(tf::Pipeflow&)>> and keep all pipes in a vector that is amenable to change. Then, it constructs a scalable pipeline using two range iterators, [first, last), that point to the beginning and the end of the pipe vector, resulting in a pipeline of three serial stages:
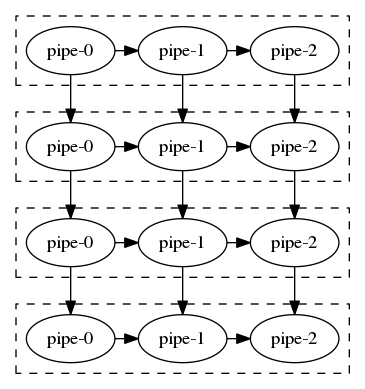
Then, the program appends another two pipes into the vector and resets the pipeline to the new range of two additional pipes, resulting in a pipeline of five serial stages:
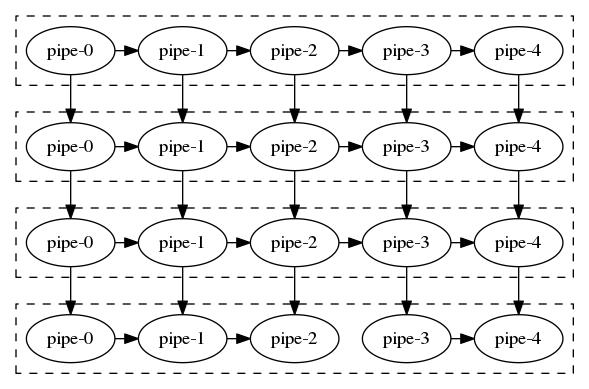
When resetting a scalable pipeline to a new range, it will start from the initial state as if it has just been constructed, i.e., the token number counts from zero.
It is possible to create a scalable pipeline as a placeholder using the constructor tf::ScalablePipeline(size_t num_lines) and reset it to another range later in the application. The following code creates a task to emplace a range of pipes and reset the pipeline to that range, before running the pipeline task:
The task graph of this program is shown below:
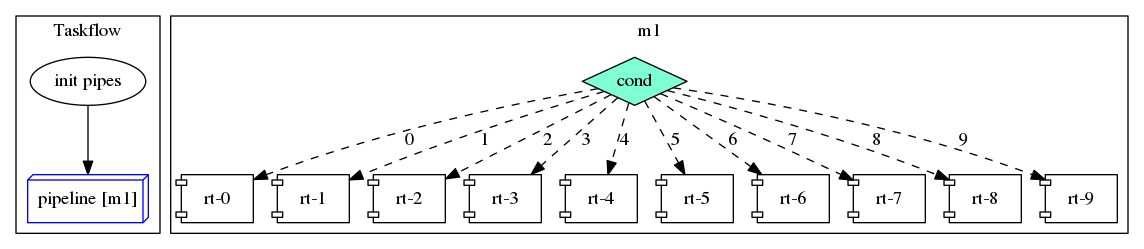
Similarly, you can create an empty scalable pipeline using the default constructor tf::ScalablePipeline() and reset it later in your program.
When assigning a range to a scalable pipeline, the pipeline fetches all pipe iterators in that range to an internal vector. This organization allows invoking a pipe callable to be a random accessible operation, regardless of the pipe container type. Taskflow does not have much restriction on the iterator type, as long as these pipes can be iterated in a sequential order using the postfix increment operator, ++.
Visit the following pages to learn more about pipeline: