 |
Taskflow
3.2.0-Master-Branch
|
 |
Taskflow
3.2.0-Master-Branch
|
Taskflow allows you to interact with the scheduling runtime from the execution context of a runtime task. Runtime tasking is mostly used for designing specialized parallel algorithms that go beyond the default scheduling rules of taskflows.
A runtime task is a callable that takes a reference to a tf::Runtime object in its argument. A tf::Runtime object is created by the running executor and contains several methods for users to interact with the scheduling runtime. For instance, the following code creates a runtime task to forcefully schedule a conditioned task that would never happens:
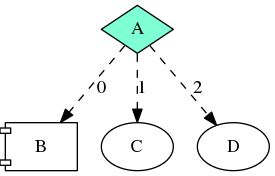
When the condition task A completes and returns 0, the scheduler moves on to the runtime task B. Under the normal circumstance, tasks C and D will not run because their conditional dependencies never happen. This can be broken by forcefully scheduling C or/and D via a runtime task that resides in the same graph. Here, the runtime task B call tf::Runtime::schedule(tf::Task) to run task C even though the weak dependency between A and C will never happen based on the graph structure itself. As a result, we will see both B and C in the output:
You can acquire the reference to the running executor using tf::Runtime::executor(). The running executor of a runtime task is the executor that runs the parent taskflow of that runtime task.